Spring中@Value的注入源码学习以及为何会产生错误数据
这是关于一次Spring中的@Value注解解析返回不正确的问题排查,以及查看Spring源码了解@Value的注入流程
问题的发生
在一次需求中,app需要我们接口返回一个配置,好让他们动态升级一些东西,这个需求很简单,我把这个东西配置在了application.yml里面,然后在程序中使用@Value注入这个内容,之后在接口中,返回这个对应的字段
1
2
a:
b: 12345
1
2
@Value("${a.b}")
private String ab;
就这样的一段非常简单的代码,但是在测试环境中,总是返回一个其他的字符串,而不是我们想要的12345。
开始排查
- 本地调试排查:本地调试了这个接口,返回正常12345
- 本地确定代码无误之后,怀疑测试环境的代码正确性,下载了测试环境的jar包,解压之后查看,代码正确,配置文件也正确
- 加入日志打印,一开始以为是在接口中,被其他东西把这个ab改了,后来发现,是在注入的时候ab就已经被注入为了其他的乱码,而不是12345
- 开始怀疑本地变量,因为@Value也会注入本地的环境变量,所以从测试环境的机器中搜索有没有a.b环境变量,发现了一个很可疑的环境变量a_b,并且里面的值就是我测试环境返回的那个错误数据
找到原因了,是因为本地变量存在了一个a_b的变量,替换了代码里面的@Value(“${a.b}”)
但是这让我发出了疑惑,@Value是怎么安排先后顺序的,并且@Value为什么会这样解析环境变量把_替换成.
查看spring源码了解底层原理
由于spring的bean创建,里面的filed注入都是在启动的时候就初始化好的,所以从spring启动开始进入源码查看
直接找到spring的refresh方法org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext#refresh
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
@Override
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
// Prepare this context for refreshing.
prepareRefresh();
// Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory.
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
// Prepare the bean factory for use in this context.
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try {
// Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses.
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
// Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context.
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Register bean processors that intercept bean creation.
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Initialize message source for this context.
initMessageSource();
// Initialize event multicaster for this context.
initApplicationEventMulticaster();
// Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses.
onRefresh();
// Check for listener beans and register them.
registerListeners();
// 初始化非懒加载的单例bean
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
// Last step: publish corresponding event.
finishRefresh();
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " +
"cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex);
}
// Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources.
destroyBeans();
// Reset 'active' flag.
cancelRefresh(ex);
// Propagate exception to caller.
throw ex;
}
finally {
// Reset common introspection caches in Spring's core, since we
// might not ever need metadata for singleton beans anymore...
resetCommonCaches();
}
}
}
进入org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext#finishBeanFactoryInitialization方法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
protected void finishBeanFactoryInitialization(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
// Initialize conversion service for this context.
if (beanFactory.containsBean(CONVERSION_SERVICE_BEAN_NAME) &&
beanFactory.isTypeMatch(CONVERSION_SERVICE_BEAN_NAME, ConversionService.class)) {
beanFactory.setConversionService(
beanFactory.getBean(CONVERSION_SERVICE_BEAN_NAME, ConversionService.class));
}
// Register a default embedded value resolver if no bean post-processor
// (such as a PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer bean) registered any before:
// at this point, primarily for resolution in annotation attribute values.
if (!beanFactory.hasEmbeddedValueResolver()) {
beanFactory.addEmbeddedValueResolver(strVal -> getEnvironment().resolvePlaceholders(strVal));
}
// Initialize LoadTimeWeaverAware beans early to allow for registering their transformers early.
String[] weaverAwareNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(LoadTimeWeaverAware.class, false, false);
for (String weaverAwareName : weaverAwareNames) {
getBean(weaverAwareName);
}
// Stop using the temporary ClassLoader for type matching.
beanFactory.setTempClassLoader(null);
// Allow for caching all bean definition metadata, not expecting further changes.
beanFactory.freezeConfiguration();
// 初始化所有的非懒加载单例bean
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
beanFactory.preInstantiateSingletons();
}
进入方法org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultListableBeanFactory#preInstantiateSingletons
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
@Override
public void preInstantiateSingletons() throws BeansException {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Pre-instantiating singletons in " + this);
}
// Iterate over a copy to allow for init methods which in turn register new bean definitions.
// While this may not be part of the regular factory bootstrap, it does otherwise work fine.
List<String> beanNames = new ArrayList<>(this.beanDefinitionNames);
// Trigger initialization of all non-lazy singleton beans...
for (String beanName : beanNames) {
RootBeanDefinition bd = getMergedLocalBeanDefinition(beanName);
if (!bd.isAbstract() && bd.isSingleton() && !bd.isLazyInit()) {
if (isFactoryBean(beanName)) {
Object bean = getBean(FACTORY_BEAN_PREFIX + beanName);
if (bean instanceof FactoryBean) {
FactoryBean<?> factory = (FactoryBean<?>) bean;
boolean isEagerInit;
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null && factory instanceof SmartFactoryBean) {
isEagerInit = AccessController.doPrivileged(
(PrivilegedAction<Boolean>) ((SmartFactoryBean<?>) factory)::isEagerInit,
getAccessControlContext());
}
else {
isEagerInit = (factory instanceof SmartFactoryBean &&
((SmartFactoryBean<?>) factory).isEagerInit());
}
if (isEagerInit) {
getBean(beanName);
}
}
}
else {
// 获取并且创建bean
getBean(beanName);
}
}
}
// Trigger post-initialization callback for all applicable beans...
for (String beanName : beanNames) {
Object singletonInstance = getSingleton(beanName);
if (singletonInstance instanceof SmartInitializingSingleton) {
SmartInitializingSingleton smartSingleton = (SmartInitializingSingleton) singletonInstance;
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedAction<Object>) () -> {
smartSingleton.afterSingletonsInstantiated();
return null;
}, getAccessControlContext());
}
else {
smartSingleton.afterSingletonsInstantiated();
}
}
}
}
进入方法org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractBeanFactory#getBean(java.lang.String)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
@Override
public Object getBean(String name) throws BeansException {
return doGetBean(name, null, null, false);
}
protected <T> T doGetBean(
String name, @Nullable Class<T> requiredType, @Nullable Object[] args, boolean typeCheckOnly)
throws BeansException {
String beanName = transformedBeanName(name);
Object bean;
// Eagerly check singleton cache for manually registered singletons.
Object sharedInstance = getSingleton(beanName);
if (sharedInstance != null && args == null) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
if (isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(beanName)) {
logger.trace("Returning eagerly cached instance of singleton bean '" + beanName +
"' that is not fully initialized yet - a consequence of a circular reference");
}
else {
logger.trace("Returning cached instance of singleton bean '" + beanName + "'");
}
}
bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(sharedInstance, name, beanName, null);
}
else {
// Fail if we're already creating this bean instance:
// We're assumably within a circular reference.
if (isPrototypeCurrentlyInCreation(beanName)) {
throw new BeanCurrentlyInCreationException(beanName);
}
// Check if bean definition exists in this factory.
BeanFactory parentBeanFactory = getParentBeanFactory();
if (parentBeanFactory != null && !containsBeanDefinition(beanName)) {
// Not found -> check parent.
String nameToLookup = originalBeanName(name);
if (parentBeanFactory instanceof AbstractBeanFactory) {
return ((AbstractBeanFactory) parentBeanFactory).doGetBean(
nameToLookup, requiredType, args, typeCheckOnly);
}
else if (args != null) {
// Delegation to parent with explicit args.
return (T) parentBeanFactory.getBean(nameToLookup, args);
}
else if (requiredType != null) {
// No args -> delegate to standard getBean method.
return parentBeanFactory.getBean(nameToLookup, requiredType);
}
else {
return (T) parentBeanFactory.getBean(nameToLookup);
}
}
if (!typeCheckOnly) {
markBeanAsCreated(beanName);
}
try {
RootBeanDefinition mbd = getMergedLocalBeanDefinition(beanName);
checkMergedBeanDefinition(mbd, beanName, args);
// Guarantee initialization of beans that the current bean depends on.
String[] dependsOn = mbd.getDependsOn();
if (dependsOn != null) {
for (String dep : dependsOn) {
if (isDependent(beanName, dep)) {
throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"Circular depends-on relationship between '" + beanName + "' and '" + dep + "'");
}
registerDependentBean(dep, beanName);
try {
getBean(dep);
}
catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"'" + beanName + "' depends on missing bean '" + dep + "'", ex);
}
}
}
// Create bean instance.
if (mbd.isSingleton()) {
// 获取单例对象
sharedInstance = getSingleton(beanName, () -> {
try {
// 函数式编程,最后又会调用这个方法来创建对象
return createBean(beanName, mbd, args);
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
// Explicitly remove instance from singleton cache: It might have been put there
// eagerly by the creation process, to allow for circular reference resolution.
// Also remove any beans that received a temporary reference to the bean.
destroySingleton(beanName);
throw ex;
}
});
bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(sharedInstance, name, beanName, mbd);
}
else if (mbd.isPrototype()) {
// It's a prototype -> create a new instance.
Object prototypeInstance = null;
try {
beforePrototypeCreation(beanName);
prototypeInstance = createBean(beanName, mbd, args);
}
finally {
afterPrototypeCreation(beanName);
}
bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(prototypeInstance, name, beanName, mbd);
}
else {
String scopeName = mbd.getScope();
if (!StringUtils.hasLength(scopeName)) {
throw new IllegalStateException("No scope name defined for bean ´" + beanName + "'");
}
Scope scope = this.scopes.get(scopeName);
if (scope == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("No Scope registered for scope name '" + scopeName + "'");
}
try {
Object scopedInstance = scope.get(beanName, () -> {
beforePrototypeCreation(beanName);
try {
return createBean(beanName, mbd, args);
}
finally {
afterPrototypeCreation(beanName);
}
});
bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(scopedInstance, name, beanName, mbd);
}
catch (IllegalStateException ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(beanName,
"Scope '" + scopeName + "' is not active for the current thread; consider " +
"defining a scoped proxy for this bean if you intend to refer to it from a singleton",
ex);
}
}
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
cleanupAfterBeanCreationFailure(beanName);
throw ex;
}
}
// Check if required type matches the type of the actual bean instance.
if (requiredType != null && !requiredType.isInstance(bean)) {
try {
T convertedBean = getTypeConverter().convertIfNecessary(bean, requiredType);
if (convertedBean == null) {
throw new BeanNotOfRequiredTypeException(name, requiredType, bean.getClass());
}
return convertedBean;
}
catch (TypeMismatchException ex) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Failed to convert bean '" + name + "' to required type '" +
ClassUtils.getQualifiedName(requiredType) + "'", ex);
}
throw new BeanNotOfRequiredTypeException(name, requiredType, bean.getClass());
}
}
return (T) bean;
}
进入org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry#getSingleton(java.lang.String, org.springframework.beans.factory.ObjectFactory<?>)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
public Object getSingleton(String beanName, ObjectFactory<?> singletonFactory) {
Assert.notNull(beanName, "Bean name must not be null");
synchronized (this.singletonObjects) {
Object singletonObject = this.singletonObjects.get(beanName);
if (singletonObject == null) {
if (this.singletonsCurrentlyInDestruction) {
throw new BeanCreationNotAllowedException(beanName,
"Singleton bean creation not allowed while singletons of this factory are in destruction " +
"(Do not request a bean from a BeanFactory in a destroy method implementation!)");
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Creating shared instance of singleton bean '" + beanName + "'");
}
beforeSingletonCreation(beanName);
boolean newSingleton = false;
boolean recordSuppressedExceptions = (this.suppressedExceptions == null);
if (recordSuppressedExceptions) {
this.suppressedExceptions = new LinkedHashSet<>();
}
try {
// 由于这里的factory使用了函数编程,所以执行在外面方法调用哪里
singletonObject = singletonFactory.getObject();
newSingleton = true;
}
catch (IllegalStateException ex) {
// Has the singleton object implicitly appeared in the meantime ->
// if yes, proceed with it since the exception indicates that state.
singletonObject = this.singletonObjects.get(beanName);
if (singletonObject == null) {
throw ex;
}
}
catch (BeanCreationException ex) {
if (recordSuppressedExceptions) {
for (Exception suppressedException : this.suppressedExceptions) {
ex.addRelatedCause(suppressedException);
}
}
throw ex;
}
finally {
if (recordSuppressedExceptions) {
this.suppressedExceptions = null;
}
afterSingletonCreation(beanName);
}
if (newSingleton) {
addSingleton(beanName, singletonObject);
}
}
return singletonObject;
}
}
进入org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory#createBean(java.lang.String, org.springframework.beans.factory.support.RootBeanDefinition, java.lang.Object[])
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
@Override
protected Object createBean(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, @Nullable Object[] args)
throws BeanCreationException {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Creating instance of bean '" + beanName + "'");
}
RootBeanDefinition mbdToUse = mbd;
// Make sure bean class is actually resolved at this point, and
// clone the bean definition in case of a dynamically resolved Class
// which cannot be stored in the shared merged bean definition.
Class<?> resolvedClass = resolveBeanClass(mbd, beanName);
if (resolvedClass != null && !mbd.hasBeanClass() && mbd.getBeanClassName() != null) {
mbdToUse = new RootBeanDefinition(mbd);
mbdToUse.setBeanClass(resolvedClass);
}
// Prepare method overrides.
try {
mbdToUse.prepareMethodOverrides();
}
catch (BeanDefinitionValidationException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(mbdToUse.getResourceDescription(),
beanName, "Validation of method overrides failed", ex);
}
try {
// Give BeanPostProcessors a chance to return a proxy instead of the target bean instance.
Object bean = resolveBeforeInstantiation(beanName, mbdToUse);
if (bean != null) {
return bean;
}
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(mbdToUse.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"BeanPostProcessor before instantiation of bean failed", ex);
}
try {
// 创建bean对象,所以这里我们在调试的时候,在断点处可以设置beanName为我们需要的那个bean,不然启动要初始化好多bean,不好排查问题
Object beanInstance = doCreateBean(beanName, mbdToUse, args);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Finished creating instance of bean '" + beanName + "'");
}
return beanInstance;
}
catch (BeanCreationException | ImplicitlyAppearedSingletonException ex) {
// A previously detected exception with proper bean creation context already,
// or illegal singleton state to be communicated up to DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry.
throw ex;
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
mbdToUse.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Unexpected exception during bean creation", ex);
}
}
进入org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory#doCreateBean,这个方法观察,在创建bean之后进行一系列对bean的初始化之后返回这个bean,所以我们的注入肯定是在这个方法中的某个调用方法实现的,我们可以通过一步步断点调用来查看bean这个对象的field是否被注入,如果前面一步没有,后面一步有了,就可以定位到是在哪个方法被注入了,我们通过排查,最后定位到了是在populateBean方法,会去初始化bean的field
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
protected Object doCreateBean(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, @Nullable Object[] args)
throws BeanCreationException {
// Instantiate the bean.
BeanWrapper instanceWrapper = null;
if (mbd.isSingleton()) {
instanceWrapper = this.factoryBeanInstanceCache.remove(beanName);
}
if (instanceWrapper == null) {
instanceWrapper = createBeanInstance(beanName, mbd, args);
}
Object bean = instanceWrapper.getWrappedInstance();
Class<?> beanType = instanceWrapper.getWrappedClass();
if (beanType != NullBean.class) {
mbd.resolvedTargetType = beanType;
}
// Allow post-processors to modify the merged bean definition.
synchronized (mbd.postProcessingLock) {
if (!mbd.postProcessed) {
try {
applyMergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessors(mbd, beanType, beanName);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"Post-processing of merged bean definition failed", ex);
}
mbd.postProcessed = true;
}
}
// Eagerly cache singletons to be able to resolve circular references
// even when triggered by lifecycle interfaces like BeanFactoryAware.
boolean earlySingletonExposure = (mbd.isSingleton() && this.allowCircularReferences &&
isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(beanName));
if (earlySingletonExposure) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Eagerly caching bean '" + beanName +
"' to allow for resolving potential circular references");
}
addSingletonFactory(beanName, () -> getEarlyBeanReference(beanName, mbd, bean));
}
// Initialize the bean instance.
Object exposedObject = bean;
try {
// 这个方法会初始化field
populateBean(beanName, mbd, instanceWrapper);
exposedObject = initializeBean(beanName, exposedObject, mbd);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
if (ex instanceof BeanCreationException && beanName.equals(((BeanCreationException) ex).getBeanName())) {
throw (BeanCreationException) ex;
}
else {
throw new BeanCreationException(
mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Initialization of bean failed", ex);
}
}
if (earlySingletonExposure) {
Object earlySingletonReference = getSingleton(beanName, false);
if (earlySingletonReference != null) {
if (exposedObject == bean) {
exposedObject = earlySingletonReference;
}
else if (!this.allowRawInjectionDespiteWrapping && hasDependentBean(beanName)) {
String[] dependentBeans = getDependentBeans(beanName);
Set<String> actualDependentBeans = new LinkedHashSet<>(dependentBeans.length);
for (String dependentBean : dependentBeans) {
if (!removeSingletonIfCreatedForTypeCheckOnly(dependentBean)) {
actualDependentBeans.add(dependentBean);
}
}
if (!actualDependentBeans.isEmpty()) {
throw new BeanCurrentlyInCreationException(beanName,
"Bean with name '" + beanName + "' has been injected into other beans [" +
StringUtils.collectionToCommaDelimitedString(actualDependentBeans) +
"] in its raw version as part of a circular reference, but has eventually been " +
"wrapped. This means that said other beans do not use the final version of the " +
"bean. This is often the result of over-eager type matching - consider using " +
"'getBeanNamesForType' with the 'allowEagerInit' flag turned off, for example.");
}
}
}
}
// Register bean as disposable.
try {
registerDisposableBeanIfNecessary(beanName, bean, mbd);
}
catch (BeanDefinitionValidationException ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Invalid destruction signature", ex);
}
return exposedObject;
}
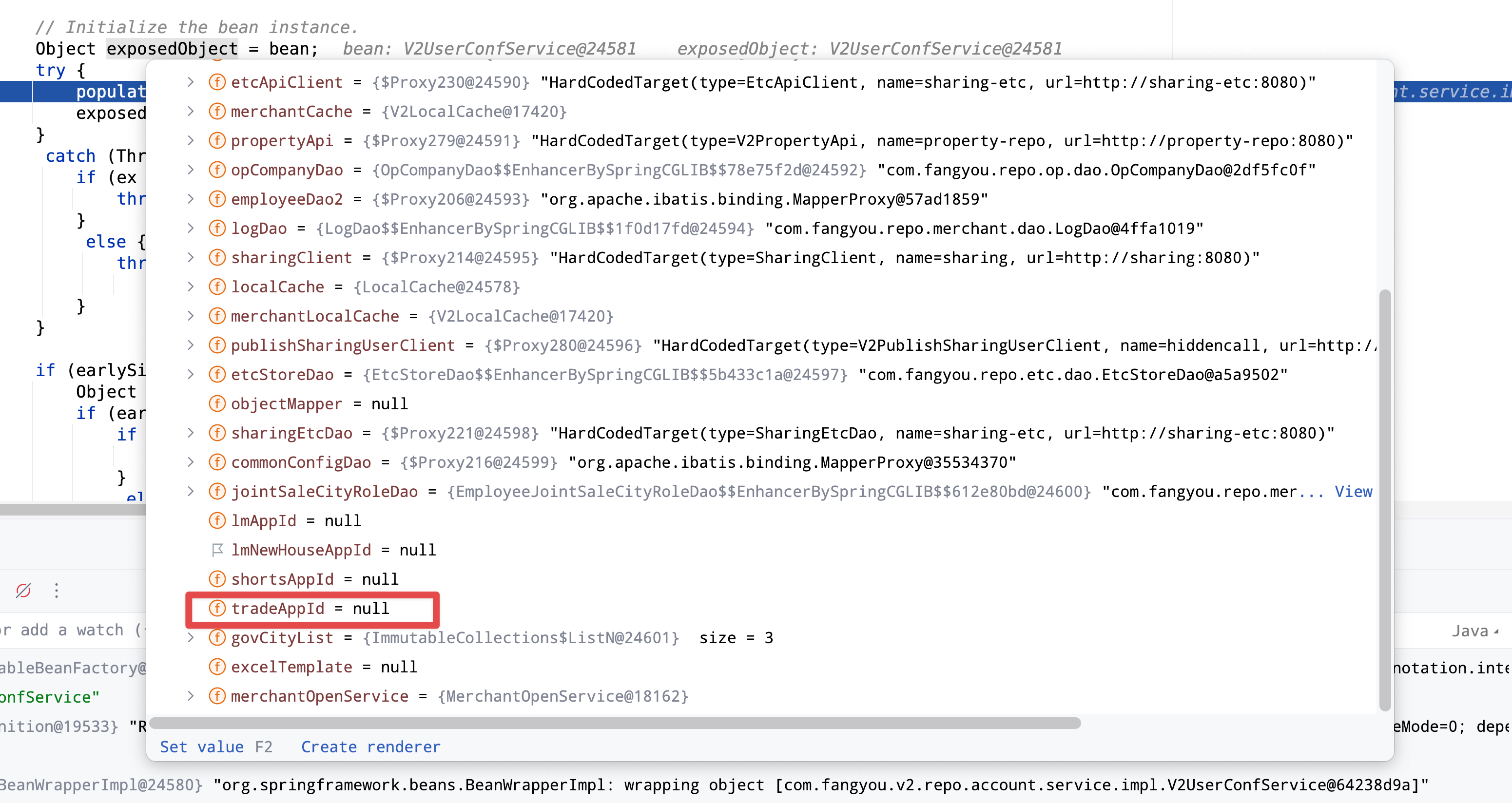
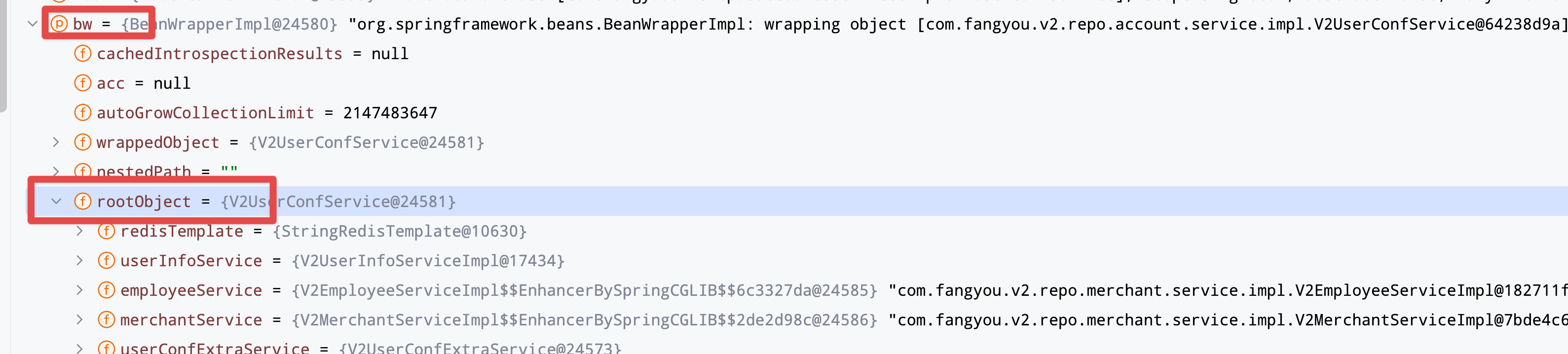
进入org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory#populateBean,由于这个方法也很长,所以我们依然使用上面一个方法来观察bean对象里面的Field是否被注入来判断到底是哪个方法调用中初始化了我们的field字段,慢慢调用之后排查到了InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor对象在其中一次执行的时候,field被初始化了,由于这个是一个for循环,所以我们还需要在for循环中具体观察是哪一次循环被初始化了,这里有一个特别说明,很多人在这个类中找不到bean对象,放在bw的rootObject里面,可以查看下图
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
protected void populateBean(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, @Nullable BeanWrapper bw) {
if (bw == null) {
if (mbd.hasPropertyValues()) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Cannot apply property values to null instance");
}
else {
// Skip property population phase for null instance.
return;
}
}
// Give any InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors the opportunity to modify the
// state of the bean before properties are set. This can be used, for example,
// to support styles of field injection.
if (!mbd.isSynthetic() && hasInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors()) {
for (BeanPostProcessor bp : getBeanPostProcessors()) {
if (bp instanceof InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) {
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor ibp = (InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) bp;
if (!ibp.postProcessAfterInstantiation(bw.getWrappedInstance(), beanName)) {
return;
}
}
}
}
PropertyValues pvs = (mbd.hasPropertyValues() ? mbd.getPropertyValues() : null);
int resolvedAutowireMode = mbd.getResolvedAutowireMode();
if (resolvedAutowireMode == AUTOWIRE_BY_NAME || resolvedAutowireMode == AUTOWIRE_BY_TYPE) {
MutablePropertyValues newPvs = new MutablePropertyValues(pvs);
// Add property values based on autowire by name if applicable.
if (resolvedAutowireMode == AUTOWIRE_BY_NAME) {
autowireByName(beanName, mbd, bw, newPvs);
}
// Add property values based on autowire by type if applicable.
if (resolvedAutowireMode == AUTOWIRE_BY_TYPE) {
autowireByType(beanName, mbd, bw, newPvs);
}
pvs = newPvs;
}
boolean hasInstAwareBpps = hasInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors();
boolean needsDepCheck = (mbd.getDependencyCheck() != AbstractBeanDefinition.DEPENDENCY_CHECK_NONE);
PropertyDescriptor[] filteredPds = null;
if (hasInstAwareBpps) {
if (pvs == null) {
pvs = mbd.getPropertyValues();
}
for (BeanPostProcessor bp : getBeanPostProcessors()) {
if (bp instanceof InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) {
// 在这个for循环中,其中一次实力话了bean的field
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor ibp = (InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) bp;
// 观察发现是AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor调用这个方法的时候初始化field
PropertyValues pvsToUse = ibp.postProcessProperties(pvs, bw.getWrappedInstance(), beanName);
if (pvsToUse == null) {
if (filteredPds == null) {
filteredPds = filterPropertyDescriptorsForDependencyCheck(bw, mbd.allowCaching);
}
pvsToUse = ibp.postProcessPropertyValues(pvs, filteredPds, bw.getWrappedInstance(), beanName);
if (pvsToUse == null) {
return;
}
}
pvs = pvsToUse;
}
}
}
if (needsDepCheck) {
if (filteredPds == null) {
filteredPds = filterPropertyDescriptorsForDependencyCheck(bw, mbd.allowCaching);
}
checkDependencies(beanName, mbd, filteredPds, pvs);
}
if (pvs != null) {
applyPropertyValues(beanName, mbd, bw, pvs);
}
}
for循环中出现了以下几个
注意,当出现AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor的时候,执行postProcessProperties方法,这个时候再去观察bean,已经被执行了,所以我们可以知道是AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor的这个方法初始化了我们的field,我们进入AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor的这个方法postProcessProperties方法org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor#postProcessProperties
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
@Override
public PropertyValues postProcessProperties(PropertyValues pvs, Object bean, String beanName) {
InjectionMetadata metadata = findAutowiringMetadata(beanName, bean.getClass(), pvs);
try {
// 在这里初始化了field
metadata.inject(bean, beanName, pvs);
}
catch (BeanCreationException ex) {
throw ex;
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(beanName, "Injection of autowired dependencies failed", ex);
}
return pvs;
}
进入inject, org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.InjectionMetadata#inject
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
public void inject(Object target, @Nullable String beanName, @Nullable PropertyValues pvs) throws Throwable {
Collection<InjectedElement> checkedElements = this.checkedElements;
Collection<InjectedElement> elementsToIterate =
(checkedElements != null ? checkedElements : this.injectedElements);
if (!elementsToIterate.isEmpty()) {
// 这里会找到类里面的所有field,进行循环每一个单独处理
for (InjectedElement element : elementsToIterate) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Processing injected element of bean '" + beanName + "': " + element);
}
element.inject(target, beanName, pvs);
}
}
}
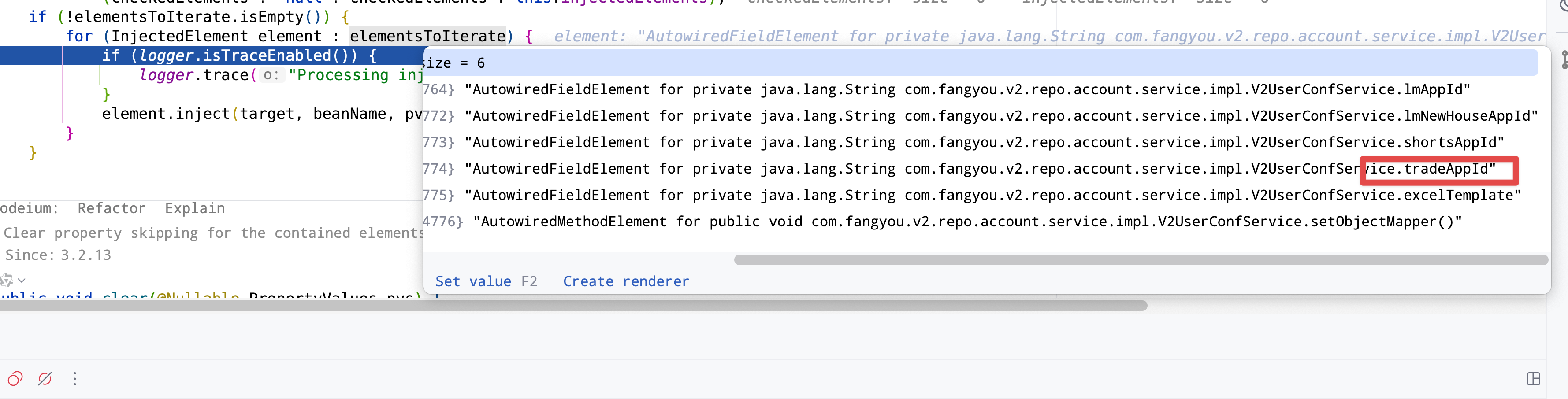
在这里我们断点发现elementsToInterate这个会找到你bean中所有需要处理的field,进行循环单独处理,查看下图,由于我们不关心其他正确的field,我们只关心我们的那个field,所以循环到我们关心的field,进行element.inject方法查看
进入org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.AutowiredFieldElement#inject,还是使用上面的一步步调用法则,最后发现在beanFactory.resolveDependency,value是解析错误的那个值,那就是这个方法了,所以进入该方法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
@Override
protected void inject(Object bean, @Nullable String beanName, @Nullable PropertyValues pvs) throws Throwable {
Field field = (Field) this.member;
Object value;
if (this.cached) {
value = resolvedCachedArgument(beanName, this.cachedFieldValue);
}
else {
DependencyDescriptor desc = new DependencyDescriptor(field, this.required);
desc.setContainingClass(bean.getClass());
Set<String> autowiredBeanNames = new LinkedHashSet<>(1);
Assert.state(beanFactory != null, "No BeanFactory available");
TypeConverter typeConverter = beanFactory.getTypeConverter();
try {
// 进行@Value注解的解析
value = beanFactory.resolveDependency(desc, beanName, autowiredBeanNames, typeConverter);
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
throw new UnsatisfiedDependencyException(null, beanName, new InjectionPoint(field), ex);
}
synchronized (this) {
if (!this.cached) {
if (value != null || this.required) {
this.cachedFieldValue = desc;
registerDependentBeans(beanName, autowiredBeanNames);
if (autowiredBeanNames.size() == 1) {
String autowiredBeanName = autowiredBeanNames.iterator().next();
if (beanFactory.containsBean(autowiredBeanName) &&
beanFactory.isTypeMatch(autowiredBeanName, field.getType())) {
this.cachedFieldValue = new ShortcutDependencyDescriptor(
desc, autowiredBeanName, field.getType());
}
}
}
else {
this.cachedFieldValue = null;
}
this.cached = true;
}
}
}
if (value != null) {
ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(field);
field.set(bean, value);
}
}
进入org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultListableBeanFactory#resolveDependency方法,最后走到了doResolveDependency
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
@Override
@Nullable
public Object resolveDependency(DependencyDescriptor descriptor, @Nullable String requestingBeanName,
@Nullable Set<String> autowiredBeanNames, @Nullable TypeConverter typeConverter) throws BeansException {
descriptor.initParameterNameDiscovery(getParameterNameDiscoverer());
if (Optional.class == descriptor.getDependencyType()) {
return createOptionalDependency(descriptor, requestingBeanName);
}
else if (ObjectFactory.class == descriptor.getDependencyType() ||
ObjectProvider.class == descriptor.getDependencyType()) {
return new DependencyObjectProvider(descriptor, requestingBeanName);
}
else if (javaxInjectProviderClass == descriptor.getDependencyType()) {
return new Jsr330Factory().createDependencyProvider(descriptor, requestingBeanName);
}
else {
Object result = getAutowireCandidateResolver().getLazyResolutionProxyIfNecessary(
descriptor, requestingBeanName);
if (result == null) {
// @Value从这里进行解析
result = doResolveDependency(descriptor, requestingBeanName, autowiredBeanNames, typeConverter);
}
return result;
}
}
进入org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultListableBeanFactory#doResolveDependency方法,由于这个方法真的很长,所以还是依然使用一步步调试的方法,发现在resolveEmbeddedValue((String) value);方法中返回了这个错误的数据,由于我们的field是string,如果是其他的,可能会有其他的流程
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
@Nullable
public Object doResolveDependency(DependencyDescriptor descriptor, @Nullable String beanName,
@Nullable Set<String> autowiredBeanNames, @Nullable TypeConverter typeConverter) throws BeansException {
InjectionPoint previousInjectionPoint = ConstructorResolver.setCurrentInjectionPoint(descriptor);
try {
Object shortcut = descriptor.resolveShortcut(this);
if (shortcut != null) {
return shortcut;
}
Class<?> type = descriptor.getDependencyType();
Object value = getAutowireCandidateResolver().getSuggestedValue(descriptor);
if (value != null) {
if (value instanceof String) {
// 解析@Value字符串
String strVal = resolveEmbeddedValue((String) value);
BeanDefinition bd = (beanName != null && containsBean(beanName) ?
getMergedBeanDefinition(beanName) : null);
value = evaluateBeanDefinitionString(strVal, bd);
}
TypeConverter converter = (typeConverter != null ? typeConverter : getTypeConverter());
try {
return converter.convertIfNecessary(value, type, descriptor.getTypeDescriptor());
}
catch (UnsupportedOperationException ex) {
// A custom TypeConverter which does not support TypeDescriptor resolution...
return (descriptor.getField() != null ?
converter.convertIfNecessary(value, type, descriptor.getField()) :
converter.convertIfNecessary(value, type, descriptor.getMethodParameter()));
}
}
Object multipleBeans = resolveMultipleBeans(descriptor, beanName, autowiredBeanNames, typeConverter);
if (multipleBeans != null) {
return multipleBeans;
}
Map<String, Object> matchingBeans = findAutowireCandidates(beanName, type, descriptor);
if (matchingBeans.isEmpty()) {
if (isRequired(descriptor)) {
raiseNoMatchingBeanFound(type, descriptor.getResolvableType(), descriptor);
}
return null;
}
String autowiredBeanName;
Object instanceCandidate;
if (matchingBeans.size() > 1) {
autowiredBeanName = determineAutowireCandidate(matchingBeans, descriptor);
if (autowiredBeanName == null) {
if (isRequired(descriptor) || !indicatesMultipleBeans(type)) {
return descriptor.resolveNotUnique(descriptor.getResolvableType(), matchingBeans);
}
else {
// In case of an optional Collection/Map, silently ignore a non-unique case:
// possibly it was meant to be an empty collection of multiple regular beans
// (before 4.3 in particular when we didn't even look for collection beans).
return null;
}
}
instanceCandidate = matchingBeans.get(autowiredBeanName);
}
else {
// We have exactly one match.
Map.Entry<String, Object> entry = matchingBeans.entrySet().iterator().next();
autowiredBeanName = entry.getKey();
instanceCandidate = entry.getValue();
}
if (autowiredBeanNames != null) {
autowiredBeanNames.add(autowiredBeanName);
}
if (instanceCandidate instanceof Class) {
instanceCandidate = descriptor.resolveCandidate(autowiredBeanName, type, this);
}
Object result = instanceCandidate;
if (result instanceof NullBean) {
if (isRequired(descriptor)) {
raiseNoMatchingBeanFound(type, descriptor.getResolvableType(), descriptor);
}
result = null;
}
if (!ClassUtils.isAssignableValue(type, result)) {
throw new BeanNotOfRequiredTypeException(autowiredBeanName, type, instanceCandidate.getClass());
}
return result;
}
finally {
ConstructorResolver.setCurrentInjectionPoint(previousInjectionPoint);
}
}
进入org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractBeanFactory#resolveEmbeddedValue方法,由于这个embeddedValueResolvers只有1个,所以直接进入这个的resolveStringValue方法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
@Override
@Nullable
public String resolveEmbeddedValue(@Nullable String value) {
if (value == null) {
return null;
}
String result = value;
for (StringValueResolver resolver : this.embeddedValueResolvers) {
result = resolver.resolveStringValue(result);
if (result == null) {
return null;
}
}
return result;
}
往下走,发现这个Resolver是一个函数对象,跳转到了org.springframework.context.support.PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer#processProperties(org.springframework.beans.factory.config.ConfigurableListableBeanFactory, org.springframework.core.env.ConfigurablePropertyResolver)里面去执行,那我们继续往下走
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
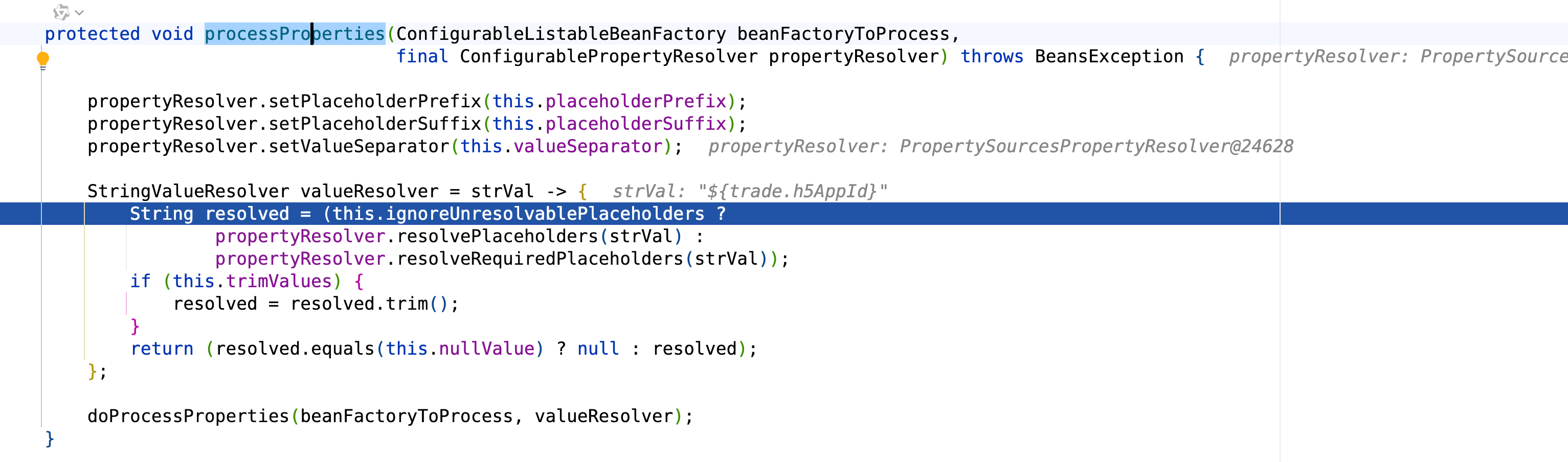
protected void processProperties(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactoryToProcess,
final ConfigurablePropertyResolver propertyResolver) throws BeansException {
propertyResolver.setPlaceholderPrefix(this.placeholderPrefix);
propertyResolver.setPlaceholderSuffix(this.placeholderSuffix);
propertyResolver.setValueSeparator(this.valueSeparator);
StringValueResolver valueResolver = strVal -> {
String resolved = (this.ignoreUnresolvablePlaceholders ?
propertyResolver.resolvePlaceholders(strVal) :
propertyResolver.resolveRequiredPlaceholders(strVal));
if (this.trimValues) {
resolved = resolved.trim();
}
return (resolved.equals(this.nullValue) ? null : resolved);
};
doProcessProperties(beanFactoryToProcess, valueResolver);
}
进入函数代码块里面之后,代码执行了propertyResolver.resolveRequiredPlaceholders(strVal)); 进行解析,所以我们进入org.springframework.core.env.AbstractPropertyResolver#resolveRequiredPlaceholders方法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
@Override
public String resolveRequiredPlaceholders(String text) throws IllegalArgumentException {
if (this.strictHelper == null) {
this.strictHelper = createPlaceholderHelper(false);
}
return doResolvePlaceholders(text, this.strictHelper);
}
从上面代码进入doResolvePlaceholders方法,org.springframework.core.env.AbstractPropertyResolver#doResolvePlaceholders
1
2
3
private String doResolvePlaceholders(String text, PropertyPlaceholderHelper helper) {
return helper.replacePlaceholders(text, this::getPropertyAsRawString);
}
继续往下org.springframework.util.PropertyPlaceholderHelper#replacePlaceholders(java.lang.String, org.springframework.util.PropertyPlaceholderHelper.PlaceholderResolver)
1
2
3
4
public String replacePlaceholders(String value, PlaceholderResolver placeholderResolver) {
Assert.notNull(value, "'value' must not be null");
return parseStringValue(value, placeholderResolver, null);
}
继续一直往下,走到了org.springframework.util.PropertyPlaceholderHelper#parseStringValue方法,又是一个大方法,发现前面是在把我们的{}里面的数据解析出来,并且在placeholderResolver.resolvePlaceholder中拿到了那个错误的数据,继续进入这个方法查看
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
protected String parseStringValue(
String value, PlaceholderResolver placeholderResolver, @Nullable Set<String> visitedPlaceholders) {
int startIndex = value.indexOf(this.placeholderPrefix);
if (startIndex == -1) {
return value;
}
StringBuilder result = new StringBuilder(value);
while (startIndex != -1) {
int endIndex = findPlaceholderEndIndex(result, startIndex);
if (endIndex != -1) {
String placeholder = result.substring(startIndex + this.placeholderPrefix.length(), endIndex);
String originalPlaceholder = placeholder;
if (visitedPlaceholders == null) {
visitedPlaceholders = new HashSet<>(4);
}
if (!visitedPlaceholders.add(originalPlaceholder)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"Circular placeholder reference '" + originalPlaceholder + "' in property definitions");
}
// 解析出来了@Value的{}的数据
// Recursive invocation, parsing placeholders contained in the placeholder key.
placeholder = parseStringValue(placeholder, placeholderResolver, visitedPlaceholders);
// Now obtain the value for the fully resolved key...
// 拿到field数据
String propVal = placeholderResolver.resolvePlaceholder(placeholder);
if (propVal == null && this.valueSeparator != null) {
int separatorIndex = placeholder.indexOf(this.valueSeparator);
if (separatorIndex != -1) {
String actualPlaceholder = placeholder.substring(0, separatorIndex);
String defaultValue = placeholder.substring(separatorIndex + this.valueSeparator.length());
propVal = placeholderResolver.resolvePlaceholder(actualPlaceholder);
if (propVal == null) {
propVal = defaultValue;
}
}
}
if (propVal != null) {
// Recursive invocation, parsing placeholders contained in the
// previously resolved placeholder value.
propVal = parseStringValue(propVal, placeholderResolver, visitedPlaceholders);
result.replace(startIndex, endIndex + this.placeholderSuffix.length(), propVal);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Resolved placeholder '" + placeholder + "'");
}
startIndex = result.indexOf(this.placeholderPrefix, startIndex + propVal.length());
}
else if (this.ignoreUnresolvablePlaceholders) {
// Proceed with unprocessed value.
startIndex = result.indexOf(this.placeholderPrefix, endIndex + this.placeholderSuffix.length());
}
else {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Could not resolve placeholder '" +
placeholder + "'" + " in value \\"" + value + "\\"");
}
visitedPlaceholders.remove(originalPlaceholder);
}
else {
startIndex = -1;
}
}
return result.toString();
}
走到了org.springframework.core.env.PropertySourcesPropertyResolver#getProperty(java.lang.String, java.lang.Class
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
@Nullable
protected <T> T getProperty(String key, Class<T> targetValueType, boolean resolveNestedPlaceholders) {
if (this.propertySources != null) {
for (PropertySource<?> propertySource : this.propertySources) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Searching for key '" + key + "' in PropertySource '" +
propertySource.getName() + "'");
}
Object value = propertySource.getProperty(key);
if (value != null) {
if (resolveNestedPlaceholders && value instanceof String) {
value = resolveNestedPlaceholders((String) value);
}
logKeyFound(key, propertySource, value);
return convertValueIfNecessary(value, targetValueType);
}
}
}
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Could not find key '" + key + "' in any property source");
}
return null;
}
最后又进入到了org.springframework.core.env.PropertySourcesPropertyResolver#getProperty(java.lang.String, java.lang.Class
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
@Nullable
protected <T> T getProperty(String key, Class<T> targetValueType, boolean resolveNestedPlaceholders) {
if (this.propertySources != null) {
for (PropertySource<?> propertySource : this.propertySources) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Searching for key '" + key + "' in PropertySource '" +
propertySource.getName() + "'");
}
Object value = propertySource.getProperty(key);
if (value != null) {
if (resolveNestedPlaceholders && value instanceof String) {
value = resolveNestedPlaceholders((String) value);
}
logKeyFound(key, propertySource, value);
return convertValueIfNecessary(value, targetValueType);
}
}
}
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Could not find key '" + key + "' in any property source");
}
return null;
}
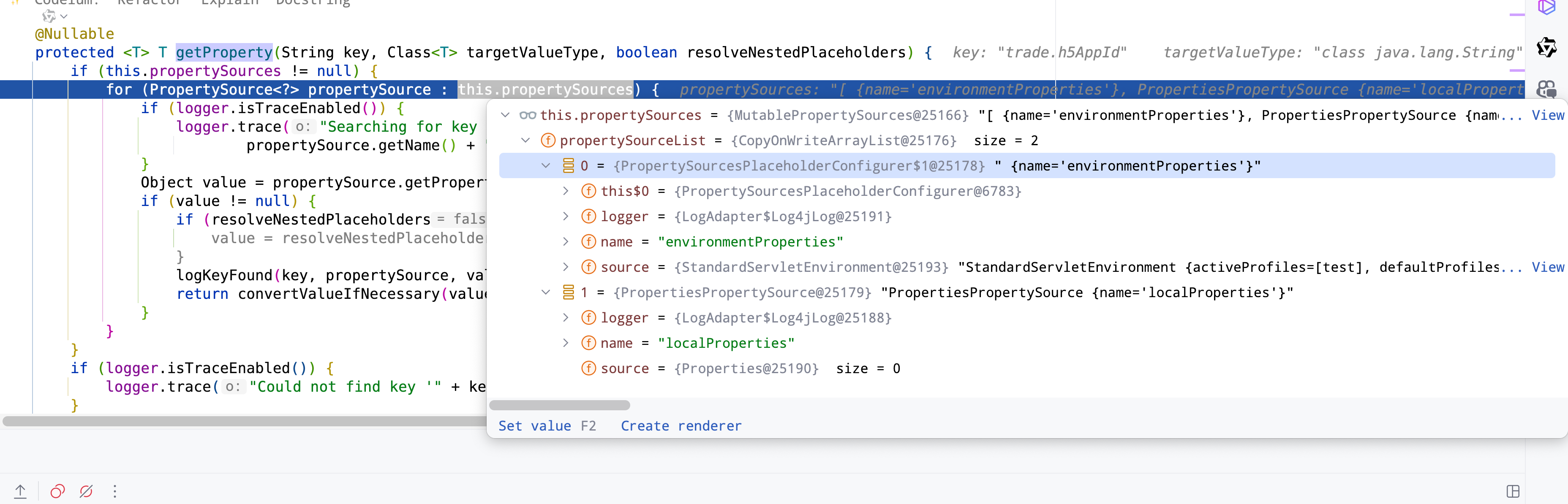
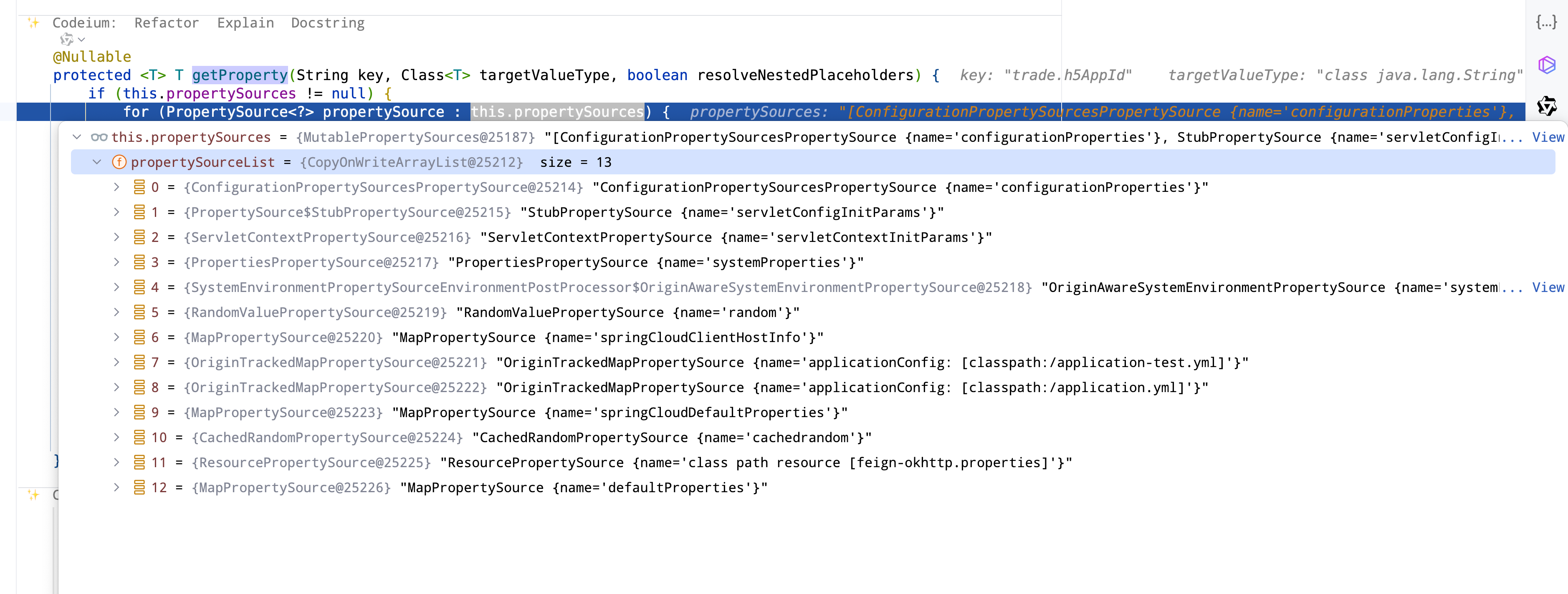
看下面的代码也是和上面一层有点像,也是通过遍历,如果先拿到则直接返回,所以这个This.propertySources里面的顺序就很重要,我们可以从这里看到,configurationProperties的顺序是最重要的,接下来是以此判断servletConfigInitParams, servletContextInitParams, systemProperties, systemEnvironment, random,等等,后面才是我们的application.yml,所以系统的配置优先级高于本地配置,这是第一点,那么接下来由于我们是environment里面的逻辑不熟悉,所以我们可以循环到environment这里,进行查看,为什么会把_解析为.
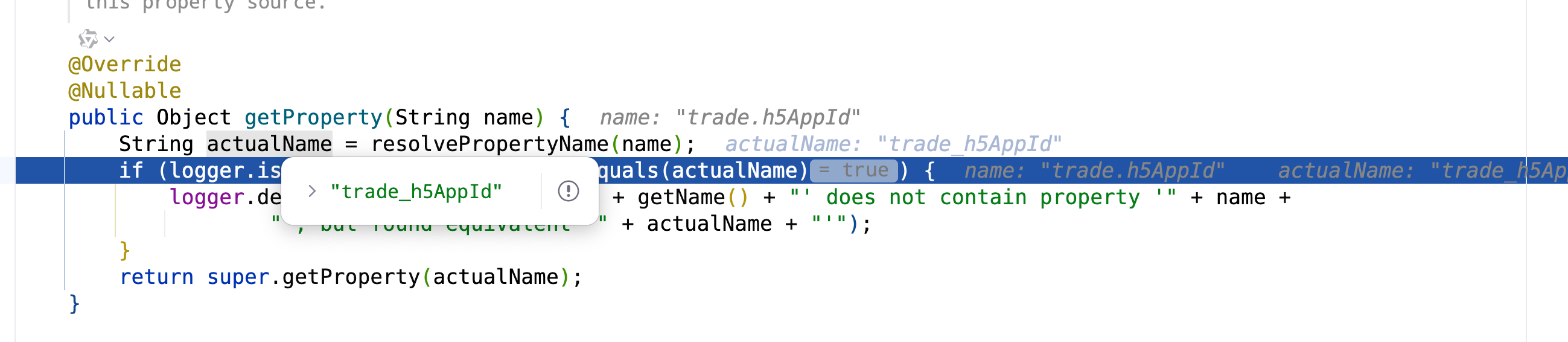
进入代码org.springframework.core.env.SystemEnvironmentPropertySource#getProperty,这个方法,我们看到会把我们的name转化为actualName,然后我们的trade.h5AppId就已经变为了trade_h5AppId,那么问题就在这个resolvePropertyName里面了
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
@Override
@Nullable
public Object getProperty(String name) {
String actualName = resolvePropertyName(name);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled() && !name.equals(actualName)) {
logger.debug("PropertySource '" + getName() + "' does not contain property '" + name +
"', but found equivalent '" + actualName + "'");
}
return super.getProperty(actualName);
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
protected final String resolvePropertyName(String name) {
Assert.notNull(name, "Property name must not be null");
String resolvedName = checkPropertyName(name);
if (resolvedName != null) {
return resolvedName;
}
String uppercasedName = name.toUpperCase();
if (!name.equals(uppercasedName)) {
resolvedName = checkPropertyName(uppercasedName);
if (resolvedName != null) {
return resolvedName;
}
}
return name;
}
@Nullable
private String checkPropertyName(String name) {
// Check name as-is
if (containsKey(name)) {
return name;
}
// Check name with just dots replaced
String noDotName = name.replace('.', '_');
if (!name.equals(noDotName) && containsKey(noDotName)) {
return noDotName;
}
// Check name with just hyphens replaced
String noHyphenName = name.replace('-', '_');
if (!name.equals(noHyphenName) && containsKey(noHyphenName)) {
return noHyphenName;
}
// Check name with dots and hyphens replaced
String noDotNoHyphenName = noDotName.replace('-', '_');
if (!noDotName.equals(noDotNoHyphenName) && containsKey(noDotNoHyphenName)) {
return noDotNoHyphenName;
}
// Give up
return null;
}
可以看到上面的代码了,是在里面做了一些特殊处理,会把.换成_, -也换成_,
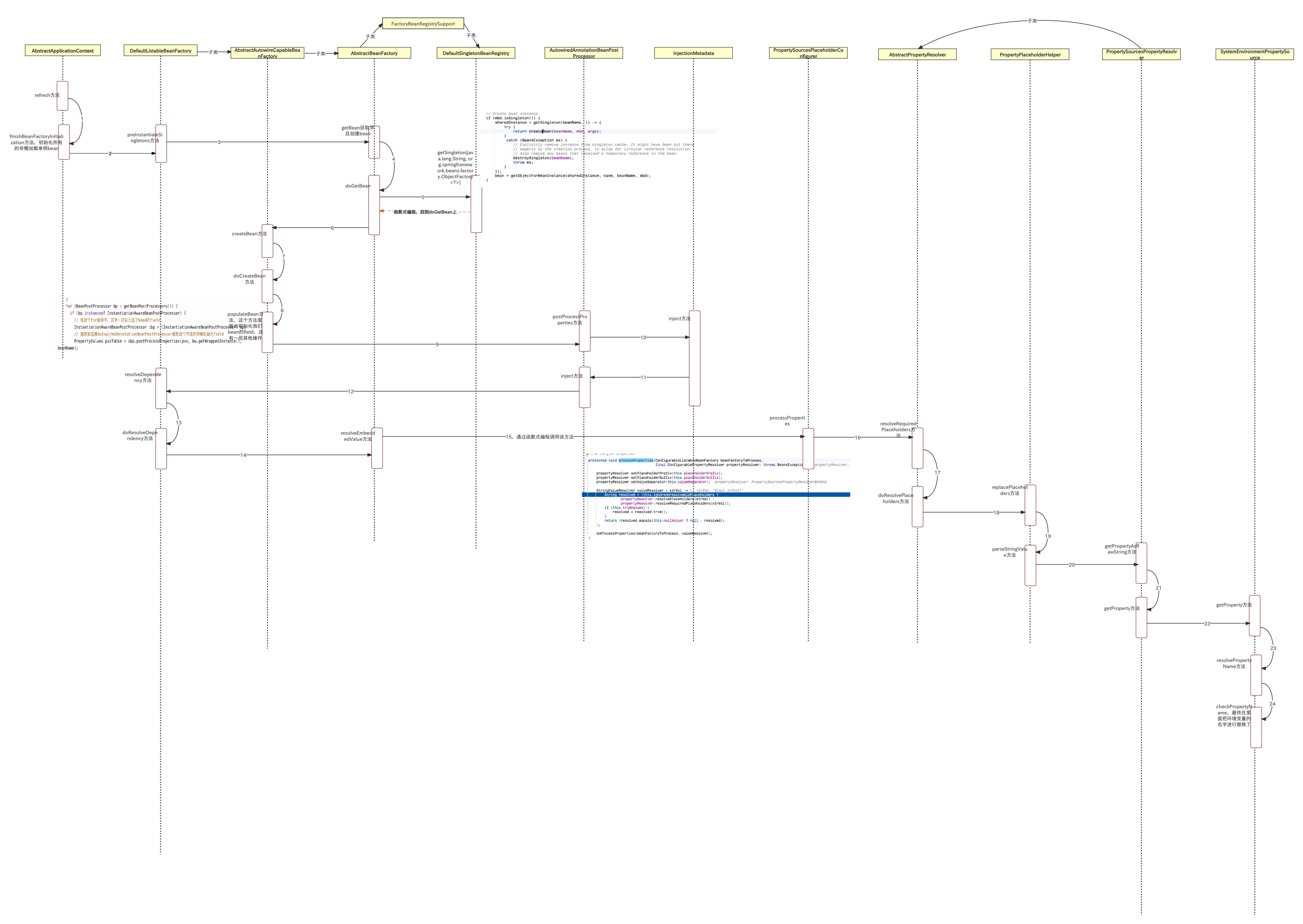
时序图
结论
可以从上面源码看出来,spring在加载@Value的时候,系统的权限顺序是大于本地application.yml的顺序的,然后当在环境变量中,这些特殊字符.,-都会变替换为_
这次的bug也是一个巧合,没想到系统变量中刚好有一个一样的,而且是.换成了_
如果不是遇到了,估计也不会在意这段代码
spring的底层源码优雅且庞大,需要有些适应过程,不然找一段代码,确实只能使用一步步调试法,但是过程中也学习到了很多,就是第一次写源码分析还是有点混乱😂
*封面图由bing image creator创建